Organizations across industries are using artificial intelligence (AI) to transform our world for the better. NASA uses AI-powered geospatial models to research climate change, the National Institutes of Health (NIH) uses treatment models to predict reactions to cancer treatments, and companies like Crusoe Energy leverage climate-aligned models to maximize resource efficiency and remove strain from electrical grids.
However, for AI to continue to make a positive impact on humanity, the companies leveraging it have growing demand for space and power paired with low latency, high bandwidth connectivity readily available when and where they need it. In other words – these forward-thinking businesses depend heavily on data centers and Internet service providers (ISPs) to innovate and make a positive difference with AI.
The Three Pillars of Transformation
The next wave of the digital revolution, marked by accelerated growth and innovation, is supported by three pillars: data centers, ISPs, and artificial intelligence. Each of these pillars is interdependent on one another, making the whole greater than the sum of its parts.
Data centers rely on connectivity into their campuses and ISPs play a critical role in their ecosystem by extending network reach beyond their facilities. Similarly, ISPs are dependent on the space, power, and cross-connects offered by data center operators to establish points of presence (PoP) which extends their network footprint – boosting both customer accessibility and peering interconnections. Combined, this attracts tenants that require reliable Internet connectivity and offers a common place for seamless network interconnections. Partnerships like this are the catalyst for growth and unlocking unrealized potential for businesses and consumers alike.
In part, it has offered Zayo the opportunity to establish over 375 IP points of presence (PoPs) globally. We each gain the benefit of facilitating traffic flows that create new value streams that enhance network scalability, reliability, and redundancy.
AI and ML applications rely on space and power from data centers for their GPU clusters which host high-performance computing environments. These computational models need access to huge amounts of public data – something tier 1 ISPs are ready and able to provide through connected IP networks. As real-world AI and ML applications increase, low latency data transfer provided by ISPs to core and edge data centers will become crucial.
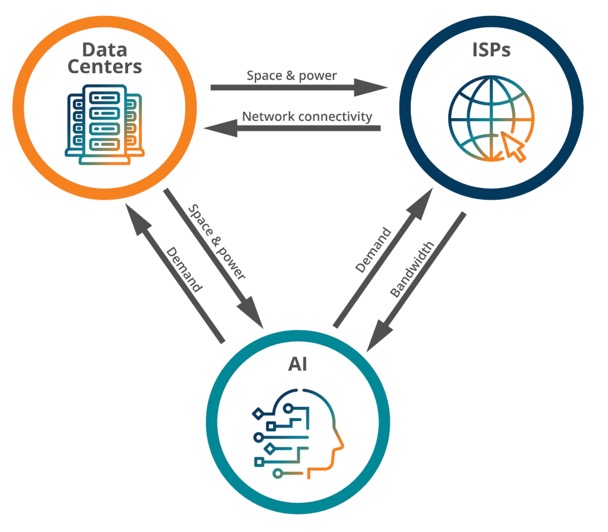
Due to these intrinsic synergies, enterprises will continue to adopt AI, and the demand for ISP and data center services will continue to rise. Today, almost three-quarters of U.S. companies have adopted AI in some areas of their business. Data center power demand is expected to grow 160% by 2030, with AI expected to represent around 19% of this skyrocketing demand by 2028. Fiber-based networks like Zayo’s are uniquely equipped to provide essential connectivity to data center locations where power is generated, leading to a demand for network services at the same time.
Data Center, ISP, and Enterprise Trends Amid the AI Boom
The historical growth of enterprise AI usage is pushing data center operators and network service providers to innovate to keep pace with demand. Here are some of the trends we’re seeing amid an unprecedented AI boom.
The Rise of GPU-as-a-Service
More enterprises are adopting GPU-as-a-Service (GPUaaS), or renting access to graphical processing units (GPUs) from service providers instead of purchasing and maintaining their own GPU hardware, which can be costly and requires technical expertise to maintain and operate. The GPUaaS market is growing rapidly, expected to reach a market value of nearly $50 billion by 2032.
GPU clusters are used to train AI models quickly and efficiently, but they require immense space and power – something that will be in short supply in the coming years. These clusters are bandwidth-intensive, and Zayo has invested actively boosting capacity in our IP core to handle the spike in demand. In 2024 alone, we’ve added over 50Tb in core capacity, to reach 158Tb – a 50% increase since the beginning of 2023 – in part to meet the needs of GPUaaS providers and their customers.
Innovators Pre-Buying Data Center Capacity
In anticipation of these constraints, hyperscalers – or large cloud service providers (CSPs) – and other market innovators are pre-buying space and power in data centers to get ahead. We’re also seeing a rise in single-tenancy in data centers as hyperscalers anticipate an upcoming shortage in data center resources. The average lead time for securing permits and construction can range anywhere from twelve to thirty-six months – and power availability is a common barrier to builds.
This trend will likely edge aspiring innovators with smaller budgets further out of traditional markets as the demand is outpacing the supply in major metros. These organizations will continue to leverage public cloud resources from hyperscalers to reduce upfront infrastructure costs and limit their own need for space and power colocate in data center facilities where space is available, or shift toward alternate markets that aren’t experiencing these challenges.
Data Center and ISP Growth in Tier 2 and 3 Markets
As demand for space and power resources outpace supply in primary markets, data center providers are looking outside of major markets, building data centers where there’s more land and power availability. Datacenter buildouts in new markets create a need for reliable network connectivity. As a result, network providers build middle-mile networks connecting high-capacity metro and long-haul fiber routes with data centers in tier 2 and 3 regions. These connections will become increasingly important as dependence on secondary market data centers grows.
While Zayo continues to expand 400G points of presence (PoPs) in tier-1 cities like Chicago and Los Angeles, power constraints are pushing demand to tier-2 and 3 metros. Markets like Hillsboro, Oregon, and Bluffdale, Utah are becoming hot spots for new data center builds as available space and power, and we’re building out our network accordingly.
Creative Solutions Emerging to Meet Space and Power Demands
Our dreams for AI-powered innovation may soon exceed the resources needed to develop them. With finite space and power resources, data center innovators are forced to get creative, generating power from new sources and finding ways to use restricted space more efficiently.
To meet power demands in the near future, data centers will likely look to renewable energy sources like geothermal, wind, and solar energy and other sources non-reliant on fossil fuels like nuclear power. The existence and ability to harness these power sources will be an important consideration as data center operators choose where to build.
Additionally, to maximize space resources, operators are finding ways to increase power per rack by increasing rack density. However, increased rack density means increased heat generation, requiring data center operators to become more innovative when it comes to cooling and airflow management. Advanced cooling technologies, environmental controls, and airflow management all become more important considerations as hardware resources in data centers become more dense.
Zayo Facilitates the AI Era with Network Solutions for What’s Next
To meet the evolving demands of the near future, ISPs will need to:
- Expand into secondary markets with fiber connections that reach data centers in tier 2 and 3 markets
- Meet bandwidth requirements boosted by large dataset transfers, thanks to AI applications, at low latency to enable real-time applications with high-capacity fiber and IP networks
- Be able to turn up additional capacity quickly, where enterprises need it to meet a rapidly evolving market demand for bandwidth in new areas
Zayo’s already looking ahead, doing all of the above and more to meet changing market needs and empower the digital revolution with:
- Connectivity into secondary and tertiary markets where data centers are expanding, enabling enterprises to meet their space and power needs in an increasingly competitive market. In 2023 alone, Zayo added 1.3 million fiber miles to our network and 2024 is off to a fast start.
- Global peering relationships and a global network with over 375 global PoPs and more than 40Tb of private peering capacity, providing low-latency business-to-business Internet connectivity.
- Continuous expansion with 25 new PoPs and connectivity into 15 markets in 2024, meeting enterprise customers wherever they need bandwidth.
- 400G investments in our growing Wavelengths and IP network – the largest 400G-enabled wavelength network in North America – to meet increasing bandwidth requirements. Around 90% of our network is 400G-enabled, and we’ve added 14 new 400G-enabled routes and 8 400G IP PoPs this year – targeting another 3 to 4 POPs in 2024.
- Access to public information through a single source with Zayo’s highly connected IP network.
- Pre-provisioned capacity at top data centers across the United States, enabling enterprises to rapidly and efficiently scale IT infrastructure as needs arise. Since January 2024, we’ve added 20 pre-provisioned data centers.
- Automated quote-to-delivery processes to ensure customers receive their orders on time. Our recently launched Waves On Demand offering on select routes allows customers to turn up Wavelengths in less than 24 hours.
- Edge networking solutions bring computations closer to key enterprise and end-user locations, lowering latency and enabling real-time end-user experiences.
- Solutions at every layer of the networking stack – from network services to cloud connectivity to edge networking solutions to security – Zayo is your one-stop networking shop.

